Last year Geosynthetica profiled NAUE’s rockfall protection wall design in Val d’Isère, a renowned winter sports region in Southeastern France. Now, the company has released video of the construction and finished work.
The geosynthetic reinforcement project enabled the Val d’Isère area, situated at 1800m above sea level, to host World Cup skiing this past winter.
The Val d’Isère Project

For the district of La Daille, boulders had increasingly broken away from the mountainside and rolled or plunged directly onto the RD 902 main road. These geohazards occasionally fell with enough energy to reach buildings in the village. The existing rockfall-protection strategies needed to be updated.
The particular challenge was to build a strong rockfall protection wall as high as possible within the limited roadside space. A steep structure was required, and it had to meet the aesthetic requirements of the resort area. The structure also needed to utilize local soils (ecological and economical benefits).
The design calculations and the execution plans for the entire construction project (with a length of 150m) were drawn up by the consultants BBG Bauberatung Geokunststoffe, Germany.
NAUE reinforcement geosynthetics were specified.
Constructing the Rockfall Protection Wall
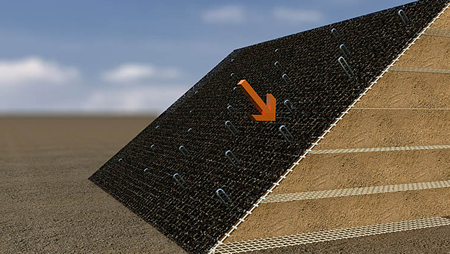
The uphill face of the structure was given a slope angle of 65° and a maximum height of 7m. The slope facing was constructed using tires, which provided robustness against rockfall impact. Secugrid® geogrids were installed every second layer of tires, with a vertical spacing of 660mm.
On the face adjacent to the road, the wall was built to approximately 12m at its highest. The lower 5m of the structure was sloped at approximately 79°. Here, Secugrid® geogrids were laid with a vertical spacing of 680mm. The facing element consisted of two layers.
The geogrids were wrapped around and a filter nonwoven was incorporated to prevent soil erosion. In front of this, an approximately 300mm-thick stacked rock facing gave the structure the aesthetic finish the site owners requested.
Permanent shuttering made of galvanized steel mesh was used over the total facing.
The upper part of the wall, with a height of up to 7m, was executed as a steep slope with an inclination of 45° (1:1). The NAUE m3 system ensured the stability of this steep slope through utilization of Secugrid® layers at a vertical spacing of 660mm. The vegetated surface was protected using erosion-protection mats.
Four different grades of NAUE Secugrid® were installed in Val d’Isère: Secugrid® 200/40 R6, Secugrid® 150/40 R6, Secugrid® 80/20 R6, and Secugrid® 40/20 R6.
Visit www.naue.com for more project stories, reinforcement designs, and other information on geosynthetics.
See also:











