The M6 Highway is one of Belarus’s 14 major motorways. It provides essential connection from the capital of Minsk to Grodno near Poland and the Bruzgi border crossing point. In the larger European roadway network, the M6 is affiliated with the E28 road. The highway system in Belarus has been undergoing substantial expansion. As part of the M6 highway improvement works, a bridge connection and overpass sited on soft soils had to be improved to prevent system instability from water leakage.
High-strength geotextiles were utilized for the works.

M6 SOFT SOILS & GEOSYNTHETIC SUPPORT
The risk of soil subsidence, asphalt cracking, and water leakage was found to be more elevated at the bridge connection and overpass construction. These types of defects are not uncommon. Transitioning smoothly from the construction of an embankment approach to more rigid design superstructures is not necessarily easy, especially when so much soil must be disturbed or brought it to make the construction possible. In the area of construction activity, the bearing capacity was not ideal. While transient concrete slabs are frequently used in situations like this, with abutment joints allowing for thermal movement, the risk of water leakage was found to be too great. It threatened the integrity of the pavement system and could impact the reinforcement in the embankments.
To better support the M6 Highway, high-strength geotextiles from Machina-TST were specified to improve the security of the embankment’s approach.
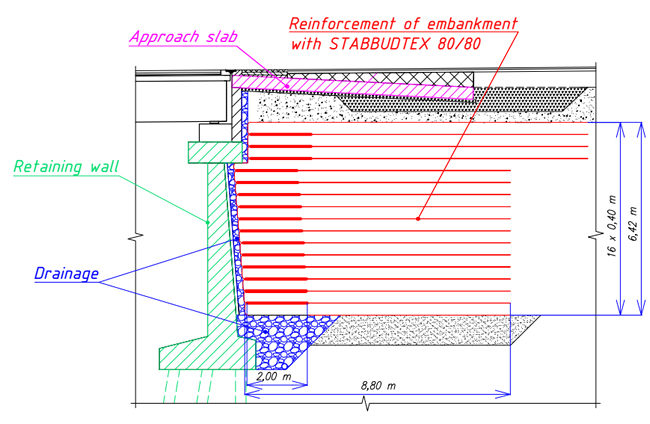
The geotextile—STABBUDTEX 80/80—was placed in 16 semi-slabs from the sandy draining soil with a pitch of 0.4 m in height. The design created a dense, highly stable ground structure to reduce vertical soil movement potential under load.
WHY IT WORKS
STABBUDTEX is a woven or warp-knitted geotextile that utilizes high-modulus polyester yarns to achieve exceptional tensile strengths (e.g., 2000 kN/m) at very low elongation. It is frequently used for embankments on soft soils, such as with this project; for hydraulic engineering (e.g., dams), steep slope and channel reinforcement; in the construction of support structures or slopes with high steepness; and to reinforce soils with low bearing capacity.

Learn more about soft soil construction strategies, geosynthetics, and more at www.mahina-tst.com.
MORE MACHINA-TST STORIES ON GEOSYNTHETICA
Halting Reflective Cracking: Machina Adds to Roadway Geosynthetics Line
Logistics Center on Geogrids in Belarus to Be New Silk Road
Asphalt Reinforcement with Geogrid on Europe’s M1 Highway











